







About Dabat Research Center
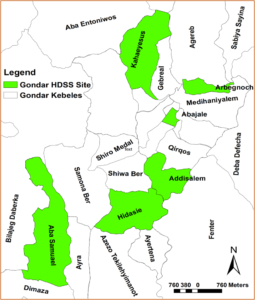
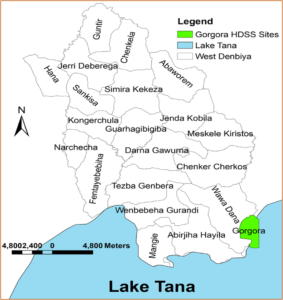
The University of Gondar has established the Dabat Health and Demographic Surveillance System (Dabat HDSS) site in 1996 (6). The HDSS site covers three geo-climatic zones (ደጋ/cold, ወይናደጋ/temperate and ቆላ/hot). Currently, the Dabat HDSS site includes 13 Kebeles (4 urban and 9 rural), over 21,000 households and 70,000 population from the Dabat district to generate longitudinal information on vital events (birth, death, migration, and marital status changes) and to estimate population-level cause of deaths using verbal autopsy method. However, the total population, the ecology diversity, and the health problems dynamicity of the Dabat district are not enough to estimate the actual health problems of Gondar. Hence, the Dabat HDSS site is expanded to Gondar and Gorgora HDSS sites considering urban population dynamicity, ecology diversity, trans-boundary population movement, and water source (e.g. Lake, Sea, and Dam) induced public health problems. The Gondar and Gorgora HDSS sites are established on April 10, 2021, after a launching workshop is conducted in the presence of top University management and stakeholders from Gondar and Gorgora.
Dabat, Gondar and Gorgora HDSS sites, collectively known as Dabat Research Center (DRC), aim to develop and evaluate a system for continuous registration of health and health-related, and socioeconomic indicators through population-level longitudinal research.
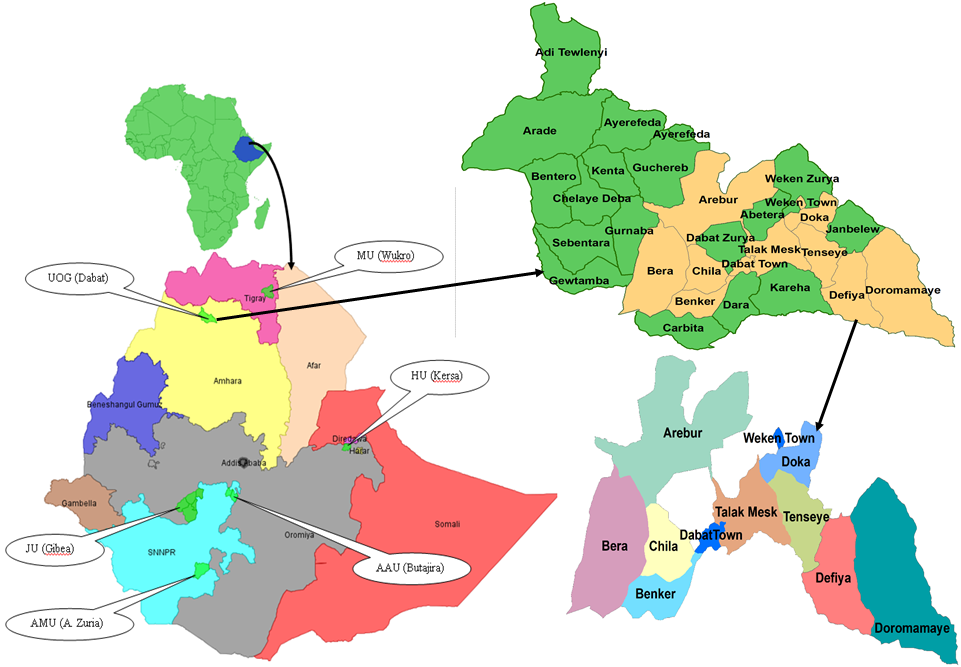
Figure: Map of Africa (top-left), Ethiopia showing regional states and six HDSS sites(bottom-left), Dabat District showing Kebeles (top-right), and HDSS site Kebeles (bottom-right).
Data Sharing
Data Sharing Policy
DRC is committed to a more open research environment, facilitating easier and faster research discovery by sharing its data to the scientific community.
Data Sharing Agreement
DRC data sharing and use agreement is a formal contract that clearly documents what data are being shared and how the data can be used.
Data Sharing Application
To submit an application, make sure to prepare an application letter, support letter from an institution, and a research proposal.






